What is RGB?
RGB stands for RedRed is the first of three primary colors in an additive color model. The "R" in RGB. More, GreenGreen is the second of three primary colors in an additive color model. The "G" in RGB. More, and BlueBlue is the third of three primary colors in an additive color model. The "B" in RGB. More. These are the colors of light. Monitors, TVs, and projectors produce images with RGB colors.
RGB is an additiveWhat is an additive color model? The RGB (red, green, blue) color model is additive. When these thre... More color modelA color model is a measurement system that numerically specifies the perceived attributes of color. More. Colors are created by adding different amounts of light together. This is in contrast to the subtractiveCMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black ) is a subtractive color model. The colors of ink added together ... More model CMYKWhat is CMYK? Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (or Key) are the four colors of ink used in four-colo... More, where colors are created by subtracting certain wavelengths of light through pigments or dyes.
Here’s how RGB works:
- Red: When red light is at its highest intensity and green and blue lights are turned off, the result is a pure red color. Lowering the intensity of red light and increasing the intensity of green and blue lights can create shades of orange and pink.
- Green: When green light is at its highest intensity and red and blue lights are turned off, the result is a pure green color. Adjusting the intensity of green light while varying the intensities of red and blue lights results in a range of greens, from lime green to teal.
- Blue: When blue light is at its highest intensity and red and green lights are turned off, the result is a pure blue color. Modifying the intensity of blue light along with the intensities of red and green lights produces various shades of blue, including indigo and turquoise.
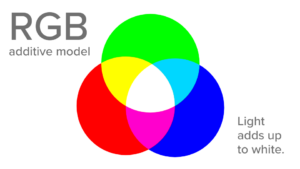
When all three colors of red, green, and blue are at their maximum intensities, they combine to create white light. When all three colors are absent (at zero intensity), the result is blackBlack is the fourth color in the process of four-color printing. The "K" in CMYK. Black adds tonal d... More.
